Search has changed fast, and 2026 makes one thing clear: Google ranking factors are no longer just about keywords or backlinks. Today, over 90% of online experiences still start with search, but how Google decides who deserves visibility looks very different than even two years ago.
With Google’s AI Overviews now taking up to 58% of clicks from top-ranking pages, clean technical SEO by itself won’t protect your traffic.
What matters now is credibility and originality!!
By this, you can prove your real experience, clear expertise, and perspectives that no automated summary can replace.
At the same time, user engagement matters more than ever. Pages that earn longer dwell time, meaningful interactions, and repeat visits send strong quality signals.
But the most notable fact is that Google has over 200 ranking factors, which might feel overwhelming to tackle. For your convenience, we’ve shortlisted the top 15 ones through our own research and testing.
How Google Ranking Factors Have Shifted (2024 → 2026)
By 2026, Google will not rank pages that mention things. It ranks pages that prove usefulness, experience, and authority.
Have a quick glance at the table below to see how Google’s core ranking priorities have changed from 2024 to 2026.
| Ranking Signal | 2024 | 2026 | Why It Matters Now |
|---|---|---|---|
| Search Intent Coverage | High | Very High | Pages must solve the entire intent, not match a query. Partial answers lose to intent‑complete pages. |
| Content Originality (Information Gain) | Medium | Very High | Generic AI‑style content is filtered out. Only new insights, experience, or data survive. |
| Author Experience (EEAT) | Low | Very High | Google now verifies who is behind the content, not just what is written. |
| Topical Authority | Medium | Very High | Single pages don’t rank alone anymore. Clusters prove real expertise. |
| Backlinks (Quality > Quantity) | High | Medium–High | Fewer, relevant, trusted links beat large, low‑quality profiles. |
| User Engagement Signals | Medium | High | Long clicks, scroll depth, and return visits validate the usefulness after AI answers. |
| Technical SEO (Core Health) | High | Medium | Required to compete, but no longer a ranking lever by itself. |
| Brand & Trust Signals | Low | High | Mentions, searches, reviews, and consistency help Google confirm legitimacy. |
15+ Google Ranking Factors That Actually Matter in 2026
I. Content & Relevance Signals
Recent industry data shows a massive divide in how Google ranks content today. Sites relying on generic “AI-assisted summaries” saw an average 22% drop in search visibility.
Conversely, pages providing “proof of execution”, such as original data or unique case studies, recorded search visibility gains of up to 18%.
1. Search Intent Match
Search intent is the specific reason behind a person’s query. In 2026, Google has moved beyond simply matching words to understanding user goals. It identifies if a user wants to learn, buy, or find a specific site.
What Is Search Intent?

Search intent is the goal behind every search query. Google analyzes billions of searches to understand what results satisfy users best.
There are four main types:
- ➜ Informational – People want to learn something
- ➜ Navigational – People want a specific website
- ➜ Commercial – People are researching before buying
- ➜ Transactional – People are ready to purchase now
For instance, traditional keyword targeting is now secondary to intent alignment. Data shows that only 8% of users click a traditional link when an AI summary satisfies their intent.
To rank today, your page must be the “final destination” for the user. High-intent satisfaction is the strongest signal for long-term ranking stability this year.
How to Optimize:
- ➜ Analyze the top 10 results for your target keyword.
- ➜ Identify the dominant content type (blog post, product page, video, list).
- ➜ Match that format exactly in your content.
- ➜ Look at what questions Google’s “People Also Ask” shows.
- ➜ Answer those questions directly in your content.
- ➜ Check if results are informational or transactional.
- ➜ Align your page structure to match that intent.
Search Intent vs Content Type (2026)
To help you understand better, here’s the comparison table describing everything we discussed earlier about the intent.
| Search Intent | Example Query | Content Type That Ranks | What Google Prioritizes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Informational | Google ranking factors | Long‑form guide | Depth & clarity |
| Commercial | Best SEO tools 2026 | Comparison page | Trust & pros/cons |
| Transactional | Buy an SEO audit | Service page | Authority & conversion |
| Navigational | Ahrefs login | Brand page | Accuracy |
2. Topical Coverage Completeness
Google’s algorithms now evaluate content like an expert editor would. They check if you’ve covered all subtopics properly.
Comprehensive pages earn more backlinks naturally. Other sites reference complete resources, not partial ones.
Time on page increases when you cover topics fully. Google sees this engagement and boosts rankings.
The Helpful Content Update specifically targets shallow content. Pages with incomplete information get filtered out aggressively. Sites with “Complete Coverage” see ranking gains up to 3x faster than those with higher domain scores but shallow content.
Complete topical coverage establishes you as an authority. Google prioritizes authoritative sources in competitive niches.
Shallow Content vs Complete Topical Coverage
One of the biggest ranking gaps in 2026 comes down to how thoroughly a topic is covered. Let’s have a quick table below:
| Factor | Shallow Content | Complete Content |
|---|---|---|
| Covered subtopics | 3–4 | 10–15+ |
| Internal links | Few | Strong topical cluster |
| Backlink attraction | Low | High |
| Average time on page | < 1 minute | 3–6 minutes |
| Ranking stability | Volatile | Long‑term |
How to Optimize for Topical Completeness:
- ➜ Build content clusters. Link a main “pillar” page to many specific “spoke” articles.
- ➜ Use the skyscraper link-building method to create superior versions of existing top-ranking content with deeper coverage
- ➜ Use semantic keywords. Include terms like “bandwidth” or “latency” when discussing internet speed.
- ➜ Internal link heavily. Connect related posts using descriptive, keyword-rich anchor text.
3. Content Freshness & Content Decay
Google loves to feature updated results for each query. The standard not only depends on the publish and update date of your page, but the system will also thoroughly cross-check the data you provide.
For example, you wrote the “Top Ranking Factors” article on your site. But all the references and sources of your data are from 2024. It will demotivate Google from trusting your info and give you a better rank.
True freshness requires updating the core facts, links, and even the media within the post.
Statistical analysis shows that pages updated within the last 6 months maintain 40% higher click-through rates than older posts.
Content Age vs Search Performance (2026)
| Last Updated | CTR Impact | Ranking Stability |
|---|---|---|
| < 3 months | Very High | Strong |
| 3–6 months | High | Stable |
| 6–12 months | Medium | Declining |
| 12+ months | Low | High risk |
How to Optimize for Content Freshness
- ➜ Refresh old stats. Replace any data point older than 12 months with the new 2026 metrics.
- ➜ Check for broken links. Fix any outbound links that lead to 404 error pages.
- ➜ Update the “Year” in titles. Ensure your headlines reflect the current calendar year.
- ➜ Add new insights. Include a “2026 Update” note to show manual oversight.
4. Semantic Term & Entity Coverage
Google’s AI models now process language like humans do. They understand synonyms, related concepts, and topic clusters.
Content with rich semantic coverage ranks higher across multiple queries. You capture long-tail variations naturally.
Entity recognition helps Google trust your expertise. Mentioning authoritative entities boosts your credibility signals.
For example, if you write about “electric vehicles,” Google expects entities like “Tesla,” “Elon Musk,” “lithium batteries,” and “charging stations.”
Missing these signals makes your content look thin. Google’s algorithm notices immediately.
Note:
The BERT and MUM algorithms specifically analyze semantic relationships. They focus on content that demonstrates deep subject knowledge.
How to Optimize for Semantic Coverage
- ➜ Use specific nouns. Replace vague words like “it” or “thing” with clear entity names.
- ➜ Add Schema Markup. Use Structured Data to tell Google exactly which entities you are discussing.
- ➜ Research Wikipedia. Check the “See Also” sections of related Wikipedia pages for essential terms.
II. Trust, Authority & Quality Thresholds
Trust is the foundation of every successful digital brand.
Google prioritizes websites that prove their credibility through verified expertise, high-quality standards, and consistent user safety.
5. Demonstrated First-Hand Experience
In 2026, the algorithm can detect if a writer has actually touched a product or lived an event. This “Experience” signal is the most recent addition to Google’s core quality framework.
It gives a good ranking to the content that includes personal stories, unique observations, and original media. If your article looks like a summary of other websites, it will fail the authenticity test.
The August 2024 Helpful Content Update hammered sites without real experience. Rankings dropped 40-60% for generic content farms.

How to Optimize:
- ➜ Use “I” and “We” statements. Describe exactly what you did during your testing.
- ➜ Upload original media. Include to prove your involvement.
- ➜ Share specific failures. Discuss what didn’t work to show honest, first-hand insight.
- ➜ Add a “How we tested” box. Briefly explain your methodology at the top of the page.
7. Author Credibility
Google uses “Author Entities” to verify that a real human expert wrote the content. The algorithm tracks an author’s footprint across the entire web to measure their reputation.
If an author has a history of writing high-quality pieces on a specific topic, their new content ranks much faster. In 2026, Google’s “Person Schema” helps the engine connect your blog to your professional awards, social profiles, and speaking engagements.
How to Optimize:
- ➜ Link to your LinkedIn. Connect your to show you are a real-world professional.
- ➜ Include a “Fact-Checked By” line. Use a second expert to verify high-stakes information.
- ➜ Claim your Google Knowledge Panel. Consolidate your digital identity into one recognized entity.
- ➜ Write a 150-word bio. Mention specific certifications, years of service, and notable achievements.
Author Trust Signals Google Tracks
These are the core author-level signals Google uses to evaluate credibility and trust.
| Signal | Importance | Practical Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Author Bio | High | Add clear credentials, years of experience, and niche focus |
| Person Schema | Very High | Use structured data to connect identity, role, and expertise |
| External Mentions | High | Earn quotes, podcast features, PR mentions, and industry citations |
| Fact‑Checker Attribution | Medium | Add a visible “Fact‑Checked By” or reviewer byline |
8. Site-Level Trust Signals
Site-level trust signals are factors that establish your website’s overall credibility. Google evaluates your entire domain’s trustworthiness.
These signals include your site’s history, ownership transparency, security, and consistency. They build a trust score for your domain.
Google looks at how long your site has existed. Brand-new sites face a “sandbox period” where rankings are limited.
Domain authority accumulates over time through quality content and clean practices. One spammy page can damage your entire site’s reputation.
How to Optimize:
- ➜ Verify your Google Business Profile. Ensure your matches across the web.
- ➜ Update your Privacy Policy. Keep your current settings to show you respect user data laws.
- ➜ Showcase real reviews. Embed third-party ratings from Trustpilot or Google to prove social proof.
- ➜ Use a secure HTTPS connection. Never let your SSL certificate expire, as this kills trust instantly.
9. YMYL Content Standards (Higher Quality Threshold)
“Your Money or Your Life” (YMYL) is a classification for topics that can significantly impact a person’s health, financial stability, or safety. In 2026, Google will use a separate, much higher quality threshold for these pages.
It is no longer enough to be “accurate”; you must be “authoritative.”
If you provide medical or financial advice without professional backing, the algorithm will actively suppress your content to protect users from potential harm.
Note:
In 2024, Google released a major algorithm update. It reduced the visibility of low-quality content by about 45%. Pages without strong authority were hit the hardest, especially in sensitive areas like health and finance. Source
How to Optimize:
- ➜ Hire expert reviewers. Add a “Medical Review” or “Legal Review” byline to your posts.
- ➜ Cite official data. Link to for all factual claims.
- ➜ Avoid “clickbait” health claims. Keep your titles objective.
- ➜ Include a clear disclaimer. State that your content is for informational purposes and not professional advice.
III. On-Site Structure & Understanding
A logical site structure acts as a roadmap for search engines. It ensures your most valuable content is easily discoverable, properly indexed, and perfectly organized.
10. Internal Page Priority
Google doesn’t treat all your pages equally. And it shouldn’t.
Your homepage matters more than a random blog post. Your money pages deserve more attention than archive pages.
Internal page priority determines which pages Google considers most important on your site. You signal this through the internal linking structure.
Pages with more internal links receive higher priority. Google crawls and indexes them more frequently.
According to a JetOctopus research summary cited in a 2026 internal linking guide, optimized internal linking improved crawl rates from ~40 % to ~70 %.
Source
How to Optimize:
- ➜ Use a “Hub and Spoke” model. Link your specific blog posts back to one main.
- ➜ Limit “Click Depth.” Ensure every important page is reachable.
- ➜ Audit orphan pages. Find and link any pages that currently have zero internal links pointing to them.
- ➜ Use descriptive anchor text. Avoid “click here”; use keywords that tell Google what the next page is about.
11. Structured Data (Schema for SERP Enhancement)
Structured data is code you add to your pages that describes your content. It uses Schema.org vocabulary that search engines understand.
Schema markup tells Google what type of content you have. Articles, products, recipes, events, and reviews each have specific markup.
This code sits in your page’s HTML. You have to identify which schema types match your content (Article, Product, Recipe, etc.).
Use Google’s Schema Markup Generator or plugins like Yoast SEO. Add JSON-LD format schema in your page head section. Also, test your markup with Google’s Rich Results Test tool.
IV. Technical Foundations & Page Experience
Technical health ensures that both users and search bots can navigate your site without friction. Here are some vital points you need to care about:
12. Crawl Accessibility
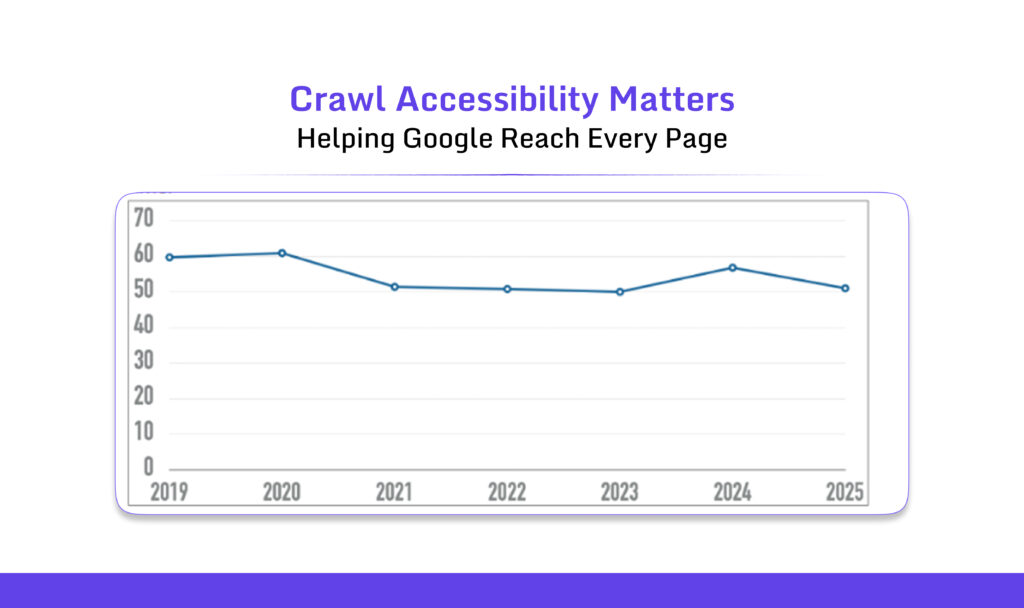
Crawl accessibility means Google’s bots can reach, read, and understand every important page on your site. Crawlers follow links to discover content. Blocked paths, broken links, or wrong settings prevent this process.
Your robots.txt file controls crawler access. One wrong line can block your entire site accidentally. XML sitemaps guide crawlers to your pages. They’re especially critical for large sites or new content.
Important:
An analysis of one million homepages found over 50 million accessibility errors, which was about 51 per page. That’s a 10.3% improvement from 2024.
These errors are serious accessibility issues that likely violate WCAG 2.2 Level A or AA standards. Source
How to Optimize Crawl Accessibility:
- ➜ Check your robots.txt file isn’t blocking important pages
- ➜ Submit an XML sitemap through Google Search Console
- ➜ Fix broken internal links that waste crawl budget
- ➜ Ensure your site loads without JavaScript errors
- ➜ Use Google Search Console’s URL Inspection tool regularly
13. Page Performance (Core Web Vitals)
Core Web Vitals are three user experience metrics Google uses for ranking. They measure loading, interactivity, and visual stability.
➔Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) measures loading speed. Your main content should load within 2.5 seconds.
➔Interaction to Next Paint (INP) replaced FID in March 2024. It measures how quickly your page responds to user interactions. Target is under 200 milliseconds.
➔Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) tracks visual stability. Elements shouldn’t jump around as the page loads. Score should stay below 0.1.
Google’s June 2021 Page Experience Update made Core Web Vitals official Google algorithm ranking factors. Sites with poor scores face ranking drops. Even more surprisingly, according to HTTP Archive’s 2024 Web Almanac, only 43% of websites pass all three Core Web Vitals.
Core Web Vitals Thresholds (2026)
These are the core web vitals signals Google uses to assess page experience quality in 2026.
| Metric | Good | Needs Improvement | Poor |
|---|---|---|---|
| LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) | ≤ 2.5s | 2.6–4s | > 4s |
| INP (Interaction to Next Paint) | ≤ 200ms | 201–500ms | > 500ms |
| CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) | ≤ 0.1 | 0.11–0.25 | > 0.25 |
To Optimize Core Web Vitals-
- ➜ Test your scores using Google PageSpeed Insights.
- ➜ Compress images to WebP format and lazy-load below-fold content
- ➜ Minimize JavaScript and defer non-critical scripts
- ➜ Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) for faster global delivery
- ➜ Implement browser caching for repeat visitors
14. Mobile-First Experience
Over 60% of all searches happen on mobile devices now. Google adapted its entire indexing system accordingly. If your mobile site is broken, your desktop perfection won’t save you. Mobile determines your rankings.
This is mobile-first indexing. Google evaluates how your site performs on smartphones and tablets. Loading speed, usability, and content accessibility on mobile devices determine rankings.
Mobile devices account for 64.35% of global website traffic as of 2025. Mobile experience includes touch-friendly buttons, readable text without zooming, and content that doesn’t require horizontal scrolling.
V. SERP, Brand & AI-Driven Signals
In 2026, search is no longer just a list of links; it is a conversation. Google’s AI now prioritizes brand reputation and entity trust over simple keyword matching.
15. SERP Format Alignment
SERP format alignment means matching your content to the specific features Google displays for your target keyword.
When you search for any term, Google shows different result types. Some queries trigger video carousels. Others show featured snippets. Local searches display map packs.
Your content must match whatever format dominates the first page. If videos rank, you need video content. If lists rank, create list-format articles.
Google shows these features based on user intent. The SERP reveals exactly what searchers want to see.
Ignoring format alignment means fighting against Google’s understanding of what works. You’ll lose every time.
16. AI Overviews (AIO) Visibility
AI Overviews are Google’s AI-generated summaries that appear at the top of search results. They synthesize information from multiple sources into one answer.
Google launched this feature globally in 2024. By 2026, it will have dominated how people search.
AI Overviews appeared in just under 25% of queries during their peak in July 2025, then pulled back to around 16% by November 2025.
These summaries pull content from 4-14 different sources. Your page might inform the answer without getting a single click.
How to Optimize for AI Overview Citations:
- ➜ Structure content with clear H2/H3 headings that match user questions exactly
- ➜ Lead every section with a concise 1-2 sentence answer (Bottom Line Up Front format)
- ➜ Use bullet points, numbered lists, and comparison tables for easy extraction
- ➜ Add FAQ schema markup to signal question-and-answer content
- ➜ Implement Article schema with author credentials and published dates
- ➜ Keep paragraphs short (2-3 sentences) for better AI parsing
17. Local SEO Trust Signals (Contextual)
Local SEO trust signals are verification factors Google uses to confirm your business is real, legitimate, and trustworthy. Google determines local rankings based on three primary factors: relevance, distance, and prominence.
According to the 2026 Local Search Ranking Factors survey, Google Business Profile signals account for approximately 32% of all map pack ranking factors.
How to Optimize:
- ➜ Master “NAP” Consistency. Ensure you are identical across your website, GBP, and directories like Yelp.
- ➜ Update Hours Weekly. Google rewards “Freshness”; are now a top-5 Google ranking signal for “open now” queries.
- ➜ Embed a Google Map. Place a to help bots confirm your precise location.
- ➜ Use LocalBusiness Schema. Explicitly tell search engines you’re using structured data.
VI. Off-Page Authority & Links
Off-page authority is the “social proof” of the internet. It validates your site’s importance through the eyes of others, proving you are a trusted industry leader.
18. Topical Relevance of Backlinks
In 2026, the old “more is better” rule for links is dead. Google now prioritizes the quality and relevance of the websites linking to you.
A single link from a high-authority industry leader like Forbes or a niche-specific journal is worth more than a thousand links from random, unrelated blogs.
Recent data shows that the top-ranking organic results have 3.8x more backlinks than those further down the page. However, understanding how many backlinks to rank depends more on your niche competitiveness and domain authority than raw numbers. In fact, comprehensive link building statistics reveal that quality and relevance now outweigh sheer volume in Google’s ranking algorithm.
To thrive in this ranking factor:
- ➜ Create “Linkable Assets.” Focus on original research, infographics, or deep-dive guides that others will use as a reference. Platforms like LinkScope can help you identify high-quality link opportunities and build topically relevant backlinks that strengthen your authority.
- ➜ Prioritize “Relevance” over “Authority.” A link from a smaller site in your specific niche is often more powerful than a generic high-authority link.
Link Types vs Ranking Impact (2026)
Not all links carry the same weight. This table breaks down how different link types impact rankings in 2026.
| Link Type | Impact Level | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Niche Editorial Link | Very High | Strong topical relevance and editorial trust |
| Brand Mention (Unlinked) | High | Helps establish entity authority and brand recognition |
| Contextual Guest Post | Medium | Value depends on site relevance and editorial depth |
| Directory Links | Low | Easily manipulated and weak trust signals |
| Forum / Comment Links | Very Low | Minimal authority, often ignored by algorithms |
19. Digital PR & Authority Mentions
Digital PR has become the most effective way to build authority this year. A staggering 48.6% of SEO experts now rate digital PR as the #1 tactic for winning high-quality links.
This is because brand mentions show a 0.664 correlation with visibility in AI-driven search, which is a higher score than traditional backlinks alone.
By being mentioned across trusted news and media sites, your brand gains an authority weight up to 2.3x higher than average mentions. For this:
- ➜ Develop data-driven reports that become go-to industry references
- ➜ Use proven link building outreach strategies to connect with journalists and industry publishers
- ➜ Target YouTube creators and podcasters for brand mentions and features
- ➜ Monitor unlinked brand mentions and convert them into citations
- ➜ Create visual assets (infographics, charts) that media outlets republish
- ➜ Focus on industry-specific publications over a generic high-DR site
How Google’s Core Updates Actually Impact Rankings
After listing the ranking factors, it’s important to know this: Google doesn’t apply them statically. Core updates rebalance their importance, which is why rankings shift without obvious technical changes.
Here are some recent Google updates that reshaped how these ranking factors are evaluated in real search results.
| Date | Main Focus | What It Impact for Rankings |
|---|---|---|
| Feb 2026 | Topic depth & relevance | Sites clearly focused on one topic performed better. Shallow or loosely related content became unstable in rankings. |
| Dec 2025 | User trust & engagement | Pages that kept users engaged and showed clear author credibility ranked more consistently across all niches. |
| Sept 2025 | Low‑quality scale & links | Mass‑produced pages and artificial link networks lost visibility, sometimes across entire sections of a site. |
| Jun 2025 | New information & freshness | Content that added genuinely new details ranked better than pages repeating what already existed in the top results. |
| Aug 2024 | Independent & original creators | Smaller sites with original, experience‑based content recovered visibility when their content showed real‑world insight. |
To Conclude
Google rankings in 2026 reward clarity, credibility, and real value, not shortcuts. Understanding how Google ranks websites means focusing on trust, originality, and user experience as a complete system.
When you align technical foundations with expert-led content and genuine usefulness, visibility follows. Optimize smarter, prove relevance, and earn clicks that actually convert.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the most important Google SEO ranking factors in 2026?
The most important Google SEO ranking factors in 2026 are content credibility, search intent satisfaction, first-hand experience, and user engagement. Technical SEO still matters, but trust and usefulness now carry more weight than ever.
2. How often do Google ranking signals change?
Google ranking signals evolve continuously through core updates, spam updates, and AI-driven refinements. While the fundamentals stay stable, the weight of SEO ranking factors in 2026 can shift several times a year.
3. Are backlinks still part of Google’s algorithm ranking factors?
Yes, backlinks are still Google algorithm ranking factors, but relevance matters more than volume. A few high-quality, niche-relevant links outperform hundreds of low-quality ones in 2026.
4. How does Google rank websites for new content?
When new content is published, Google evaluates topical relevance, freshness, internal linking, and early user behavior. Understanding how Google ranks websites early helps pages gain traction faster and avoid ranking decay.




